*Eligible patients may pay a minimum of $0 and receive up to $2,000 off the patient’s co-pay or out-of-pocket expenses per prescription fill of PANCREAZE (pancrelipase) capsules with a maximum yearly benefit of $3,500. Out-of-pocket expenses may vary. Click here for more information.
PANCREAZE is indicated for the treatment of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency in adult and pediatric patients.
Fibrosing Colonopathy: Associated with high doses, usually over prolonged use and in pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis. Colonic stricture reported in pediatric patients less than 12 years of age with dosages exceeding 6,000 lipase units/kg/meal. Monitor during treatment for progression of preexisting disease. Do not exceed the recommended dosage, unless clinically indicated.
Hyperuricemia has been reported with high dosages; consider monitoring blood uric acid levels in patients with gout, renal impairment, or hyperuricemia.
Irritation of the oral mucosa may occur due to loss of protective enteric coating on the capsule contents.
The presence of porcine viruses that might infect humans cannot be definitely excluded.
Monitor patients with known reactions to proteins of porcine origin. If symptoms occur, initiate appropriate medical management; consider the risks and benefits of continued treatment.
Please read the PANCREAZE Medication Guide and PANCREAZE Product Information.
References:
1. PANCREAZE Full Prescribing Information. Campbell, CA: VIVUS LLC; 2024.
2. Trapnell BC, Strausbaugh SD, Woo MS, et al. Efficacy and safety of PANCREAZE for treatment of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency due to cystic fibrosis. J Cyst Fibros. 2011;10(5):350-356.
3. Fieker A, Philpott J, Armand M. Enzyme replacement therapy for pancreatic insufficiency: present and future. Clin Exp Gastroenterol. 2011;4:55-73.
4. Whitcomb, DC, Buchner, AM, Forsmark, CE. AGA Clinical Practice Update on the Epidemiology, Evaluation, and Management of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency: Expert Review. Gastroenterology. 2023;165:1292–1301.
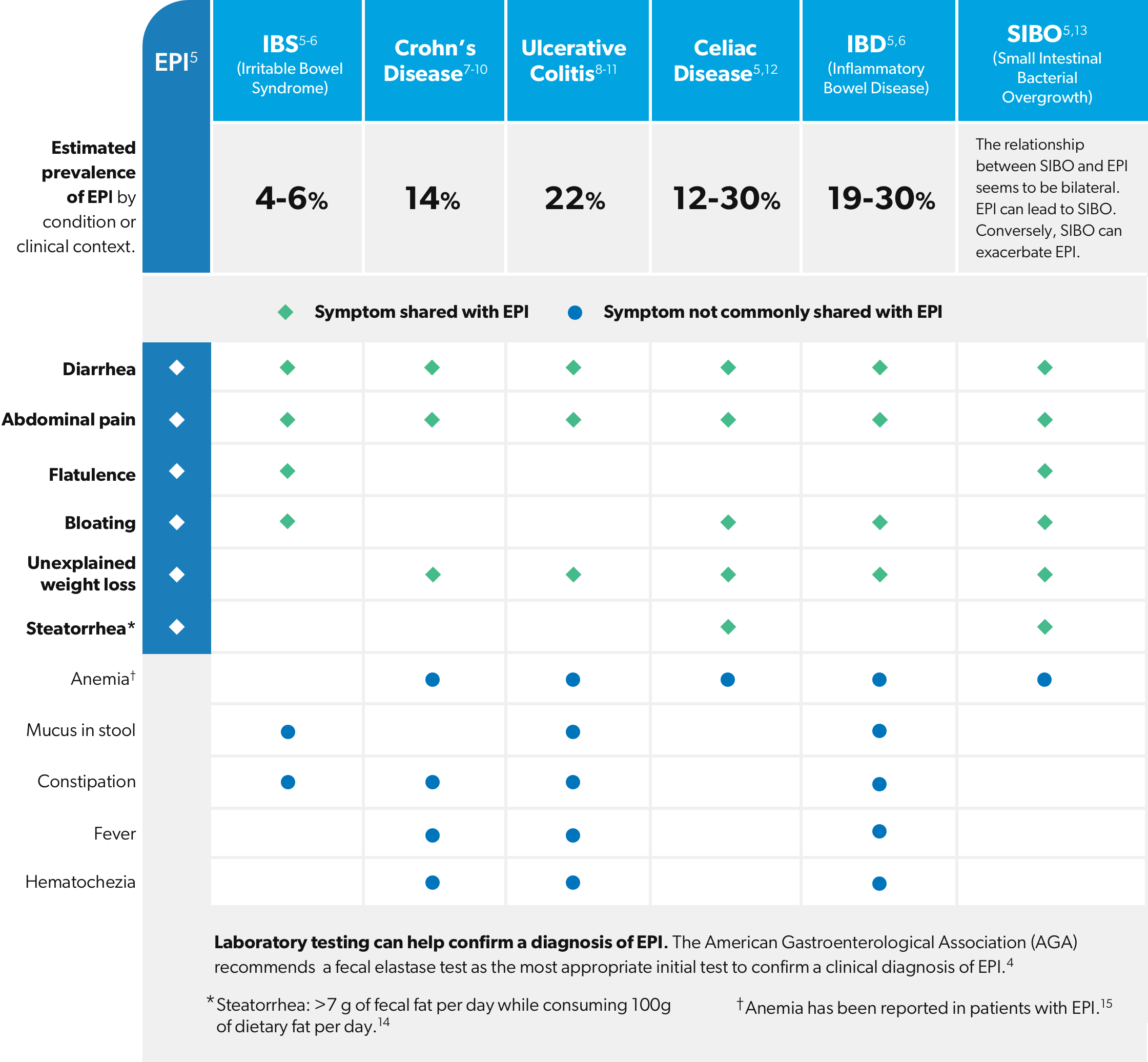
5. Othman MO, Harb D, Barkin JA. Introduction and practical approach to exocrine pancreatic insufficiency for the practicing clinician. Int J Clin Pract. 2018;72:e13066.
6. Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation (n.d). IBS vs IBD. Retrieved from https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/what-is-ibd/ibs-vs-ibd
7. Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation (n.d). Signs and Symptoms of Crohn’s Disease. Retrieved from https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/what-is-crohns-disease/symptoms
8. Kaitha S, Bashir M, Ali T. Iron deficiency anemia in inflammatory bowel disease. World J Gastrointest Pathophysiol. 2015 August 15; 6(3): 62-72.
9. Perler BK, Ungaro R, Baird G, et al. Presenting symptoms in inflammatory bowel disease: descriptive analysis of a community-based inception cohort. BMC Gastroenterology (2019); 19:47.
10. Fousekis FS, Theopistos VI, Katsanos KH, Christodoulou DK. Pancreatic Involvement in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Review. J Clin Med Res. 2018;10(10):743-751.
11. Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation (n.d). Signs and Symptoms of Ulcerative Colitis. Retrieved from https://www.crohnscolitisfoundation.org/what-is-ulcerative-colitis/symptoms
12. Freeman HJ. Iron deficiency anemia in celiac disease. World J Gastroenterol. 2015 August 21; 21(31):9233-9238.
13. Zaidel O, Lin HC. Uninvited Guests: The Impact of Small Intestinal Bacterial Overgrowth on Nutritional Status. Practical Gastroenterology. 2003; Nutrition Issues in Gastroenterology, Series #7: 23-34.
14. Struyvenberg MR, Martin CR, Freedman SD. Practical guide to exocrine pancreatic insufficiency – Breaking the myths. BMC Med. 2017; 15(1): 29.
15. Al-Kaade S, Khardori R (2020, February 3). What causes anemia in exocrine pancreatic insufficiency (EPI)? Medscape. Retrieved from https://www.medscape.com/answers/2121028-18736/what-causes-anemia-inexocrinepancreatic-insufficiency-epi
16. Vujasinovic M, Valente R, Thorell A, et al. Pancreatic Exocrine Insufficiency after Bariatric Surgery. Nutrients. 2017 Nov 13;9(11):1241.
17. Uribarri-Gonzalez L, Nieto-García L, Martis-Sueiro A, et al. Exocrine pancreatic function and dynamic of digestion after restrictive and malabsorptive bariatric surgery: a prospective, cross-sectional, and comparative study. Surg Obes Relat Dis. 2021 Oct;17(10):1766-1772.
18. The National Pancreas Foundation (n.d.). Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency (EPI). Retrieved from https://pancreasfoundation.org/patient-information/ailments-pancreas/exocrine-pancreatic-insufficiency-epi/
19. Cystic Fibrosis Foundation. (n.d.). Phthalates. Retrieved from https://www.cff.org/phthalates.
20. CREON® Full Prescribing Information. Chicago, IL: AbbVie, Inc; 2024.
21. PERTZYE® Full Prescribing Information. Bethlehem, PA: Digestive Care, Inc; 2024.
22. VIOKACE™ Full Prescribing Information. Birmingham, AL: Allergan USA, Inc; 2012.
23. ZENPEP® Full Prescribing Information. Bridgewater, NJ: Aimmune Therapeutics, Inc; 2024.
24. Huang W, Iglesia‑Garcia DDL, Baston‑Rey I, et al. Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency Following Acute Pancreatitis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Jul;64(7):1985-2005.
25. Phillips, Anna Evans, Bejjani, J, Culp S, et al. Prevalence of exocrine pancreatic insufficiency at 12 months after acute pancreatitis: a prospective, multicentre, longitudinal cohort study. eClinicalMedicine, Volume 75, Sep 2024,102774.
26. Radlinger B, Ramoser, G and Kaser S. Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency in Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes. Current Diabetes Reports. 2020;20:18.
27. Martin TCS, Scourfield A, Rockwood N, et al. Pancreatic insufficiency in patients with HIV infection: role of didanosine questioned. HIV Medicine (2013),14,161-166.
28. Price DA, Schmid ML, Ong ELC, et al. Pancreatic exocrine insufficiency in HIV-positive patients. HIV Medicine (2005),6,33–36.
29. Brennan GT, Saif MW. Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy: A Concise Review. JOP. 2019;20(5):121-125. 30. Barkin JA, Harb D, Kort J, Barkin J. Real-World Patient Experience With Pancreatic Enzyme Replacement Therapy in the Treatment of Exocrine Pancreatic Insufficiency. Pancreas. 2024 Jan 1;53(1).